If you’re here, chances are you’re seeking clarity on the mysterious world of SWOT analysis. Perhaps you’re a business enthusiast looking to enhance your strategic planning skills or a professional eager to unravel the layers of this powerful tool. Fear not, for this blog is your guiding light through the SWOT maze! We understand your curiosity and desire for a straightforward, user-friendly guide. Join us on a journey to demystify SWOT analysis, where we’ll break down its basics, components, and benefits. This blog is your go-to resource to have a crystal-clear understanding of how to wield the SWOT magic. Let’s dive in together!
In-Depth Handbook to SWOT Analysis

What is SWOT Analysis?
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps organizations identify their internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. By examining these four key components, businesses can clearly understand their current position and make informed decisions about future strategies.
Imagine SWOT analysis as a special pair of glasses for businesses. These glasses help organizations see four important things: their superpowers (strengths), areas where they need to improve (weaknesses), exciting opportunities around them (opportunities), and potential challenges or dangers (threats).
So, when a company puts on these SWOT glasses, it can better understand itself and its surroundings. For example, it might realize it has a fantastic team (strength) but needs better technology (weakness). It might also spot a chance to grow in a new market (opportunity) but notice tough competition (threat).
Examining these four aspects empowers businesses to make informed decisions about their current state and plan for the future. SWOT analysis serves as a roadmap, guiding them on their journey to success. For expert guidance in strategic planning, consider Canada assignment help to navigate the path to success with precision and expertise.
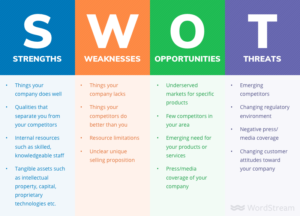
Components of SWOT Analysis:
-
Strengths:
Strengths are like the superpowers your organization possesses. These are the internal factors that make your business stand out from the crowd. It could be having a team of highly skilled and motivated individuals, a strong and recognized brand, cutting-edge technology that gives you an edge, or super-efficient processes that make everything run smoothly. Identifying strengths helps you understand what you’re good at.
-
Weaknesses:
Weaknesses are the areas where your organization might not be at its best. These are internal aspects that could hold you back. It might be using outdated technology that slows down your work, not having enough skilled people for certain tasks, or having processes that could be more efficient. Recognizing weaknesses is the first step to improving and growing stronger.
-
Opportunities:
Opportunities are like open doors for your organization. These are external factors in the world around you that you can use to your advantage. It could be a new trend in the market that aligns with your products or services, advancements in technology that you can adopt, or changes in regulations that create room for your business to grow. Exploring opportunities allows you to chart a path for expansion and success.
-
Threats:
Threats are the challenges that come knocking on your organization’s door from the outside. These are external factors that could potentially harm your business. It might be an economic downturn affecting people’s spending habits, new competitors entering the scene, or shifts in consumer behavior that don’t favor your products or services. Considering threats helps you prepare and navigate through rough waters, ensuring you’re ready for whatever challenges come your way.
Benefits of SWOT Analysis:
- Strategic Planning: Foundation for strategy, aligning resources with goals for effective long-term planning.
- Risk Management: Proactive threat identification, empowering businesses to address challenges and minimize risks efficiently.
- Decision Making: Informed decisions emerge from comprehensive SWOT analysis, guiding strategies based on strengths, opportunities, weaknesses, and threats.
- Performance Improvement: Pinpointing weaknesses allows targeted improvements, enhancing overall organizational performance.
- Resource Optimization: Efficiently allocate resources by leveraging strengths and seizing opportunities while addressing weaknesses and mitigating threats.
- Competitive Advantage: Gain a competitive edge by strategically positioning the business, leveraging strengths, and navigating challenges effectively.
[You can also read: List of 100 Case Study Topics Ideas]
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis:
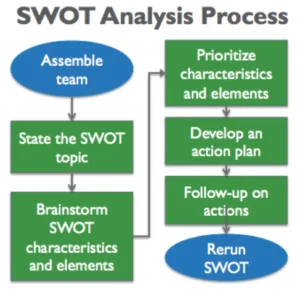
- Gather a Diverse Team:
To build a diverse team for a comprehensive analysis, gather individuals from different departments within your organization. This inclusivity is crucial as diverse perspectives bring a variety of insights to the table. Ensure representation from departments such as marketing, finance, operations, and customer service to cover a broad range of expertise. Encourage inclusivity, consider various skill sets and job levels, and foster collaboration between departments. By assembling a team with diverse backgrounds and experiences, you create an environment that promotes creativity, thoroughness, and a more holistic approach to the task at hand. - Brainstorm Each Component:
Certainly! Let’s break down the detailed steps on how to effectively brainstorm each component in a SWOT analysis:- Set the Stage: Begin by setting the purpose of the brainstorming session: to identify factors for each SWOT category. Emphasize the importance of open communication and a collaborative atmosphere.
- Define Each Category: Clearly explain the four categories: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Provide examples for better understanding.
- Create a Comfortable Environment: Foster an open and inclusive environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts. Reinforce that all ideas are welcome, and there are no right or wrong answers.
- Use Visualization Aids: Employ whiteboards, flip charts, or online collaboration tools to visually document ideas. Visual aids help everyone see and engage with the evolving discussion.
- Start with Strengths: Initiate the discussion by focusing on internal strengths. Encourage team members to share what the organization excels at. Ask probing questions like: “What do we do better than anyone else?” or “What are our core competencies?”
- Explore Weaknesses: Transition to internal weaknesses. Prompt the team to identify areas for improvement or challenges. Ask questions such as: “What obstacles do we face internally?” or “Where do we have room to grow?”
- Shift to Opportunities: Move to external opportunities. Encourage team members to think about positive external factors that could benefit the organization. Pose questions like: “What trends in the market can we leverage?” or “Are there untapped opportunities in our industry?”
- Discuss Threats: Conclude by exploring external threats. Prompt the team to consider potential challenges or risks in the external environment. Ask questions like: “What external factors might impact us negatively?” or “Are there emerging threats in the industry?”
- Facilitate Active Participation: Ensure everyone has an opportunity to contribute. Use techniques like round-robin or go-around to encourage input from all team members.
- Capture Ideas Efficiently: Record ideas succinctly but comprehensively on the chosen visualization aid. Avoid judgment or discussion at this stage; focus on gathering a wide range of ideas.
- Encourage Discussion: After initial brainstorming, open the floor for discussion. Encourage team members to elaborate on their ideas and build upon each other’s insights.
- Prioritize and Clarify: Facilitate a discussion to prioritize key factors within each category. Clarify any ambiguous points and ensure a shared understanding of each idea.
- Document and Summarize: Document the finalized list of factors for each category. Summarize key insights and potential themes that emerge from the discussion.
- Reflect and Follow-Up: Reflect on the outcomes of the brainstorming session. Schedule a follow-up session to refine, validate, and discuss strategies based on b the identified factors.
- Prioritize and Analyze:
To initiate a comprehensive SWOT analysis, the first step is a meticulous prioritization and analysis of identified factors. Begin by scrutinizing each factor, discerning its importance and impact on organizational goals. This evaluation considers both internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. By encompassing both internal and external elements, a holistic perspective of the organization’s landscape emerges.The prioritization process involves a systematic ranking, assigning scores or categorizations based on predefined criteria. This structured approach objectively assesses each factor’s significance. Importance reflects its relevance to overarching organizational objectives, while impact gauges the potential effects on performance, growth, or goal achievement.This dual consideration of importance and impact aids in unveiling critical areas that demand strategic focus. The analysis identifies key factors that become focal points for subsequent decision-making and planning. These prioritized elements guide the organization with precision, ensuring resources are directed toward addressing weaknesses, leveraging strengths, capitalizing on opportunities, and mitigating threats effectively. - Identify Relationships:
Delve deeper into your analysis by exploring the intricate relationships between internal strengths, weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats. Understanding these connections adds valuable context to your assessment, revealing potential synergies, dependencies, and strategic implications. This step fosters a more nuanced understanding of how your organization’s internal dynamics interact with external forces, contributing to a more informed SWOT analysis.
- Develop Strategies:
With a clear picture, formulate strategies. Capitalize on strengths and opportunities, address weaknesses, and devise plans to mitigate potential threats.- Leverage Strengths and Opportunities: Begin the strategy development phase by identifying how your organization’s strengths and opportunities can be synergized. Capitalize on existing competencies, whether it’s a skilled workforce, advanced technology, or a strong brand reputation. Explore avenues where your strengths align with external opportunities for maximum impact.
- Address Weaknesses: Devote attention to addressing weaknesses uncovered in the SWOT analysis. Develop strategies that enhance internal processes, skillsets, or technological capabilities. This might involve training programs, process improvements, or investments in technology to fortify areas of vulnerability.
- Mitigate Potential Threats: Formulate robust plans to proactively mitigate potential threats. Whether economic downturns, emerging competitors, or regulatory changes, strategize ways to navigate and minimize the impact of external threats. This could include contingency plans, diversification strategies, or partnerships to enhance resilience.
- Align Resources and Capabilities: Ensure that developed strategies align seamlessly with your organization’s available resources and capabilities. Assess the feasibility and practicality of implementing the strategies, considering factors such as budget constraints, personnel expertise, and technological infrastructure. This alignment guarantees a realistic and executable approach.
- Proactive Approach to Goals: Craft strategies that not only address immediate concerns but also align with broader organizational goals. This forward-thinking approach ensures that strategies are not only reactive but contribute to the long-term vision of the organization. Aligning strategies with overarching goals fosters sustained success and growth.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Acknowledge that the business landscape is dynamic, requiring strategies that are adaptable and flexible. Build in mechanisms for periodic review and adaptation of strategies based on evolving circumstances. An agile approach allows the organization to stay responsive to changing internal and external factors, ensuring continued relevance and effectiveness.
- Seek Feedback:
Imagine your company wants to explore a new market by using its strong brand reputation and responding to what customers want. After figuring out this plan through a SWOT analysis, it’s really important to get thoughts from your team to make it even better.
So, gather your team members from different parts of the company, like marketing, operations, finance, and sales. Show them the plan and ask for their ideas. For example, someone who knows about customers might share helpful information, and another person might talk about how things work behind the scenes.
By doing this, you’re using everyone’s knowledge to make the plan stronger. Maybe the finance team will point out money challenges, and the sales team might notice things competitors are doing. This teamwork refines and checks the plan, making it stronger and more practical. It’s crucial because getting feedback not only improves your plans but also makes your team feel more involved. This way, everyone works together to make better decisions and reach success.
SWOT Analysis Examples:

-
Strengths:
- Strong Brand Recognition: Example: A well-established logo, positive customer perceptions, and a history of delivering quality products contribute to a strong brand, fostering customer loyalty and trust.
- Skilled and Motivated Workforce: Example: A team with diverse talents, high morale, and a strong work ethic creates an environment where innovation flourishes, leading to increased productivity and overall organizational success.
-
Weaknesses:
- Outdated IT Infrastructure: Example: Having outdated software and hardware can lead to inefficiencies, slow processes, and increased vulnerability to cyber threats, hindering the organization’s ability to adapt to technological advancements.
- Limited Marketing Budget: Example: A constrained budget for advertising and promotions may limit the organization’s ability to reach a wider audience, potentially affecting market visibility and customer acquisition.
-
Opportunities:
- Growing Market Demand for Eco-friendly Products: Example: As environmental concerns rise, there’s an opportunity to develop and market eco-friendly products, tapping into a growing consumer segment focused on sustainable and environmentally conscious choices.
- Emerging Markets in Developing Countries: Example: Identifying and entering untapped markets in developing countries can open avenues for expansion, capturing new customers and establishing a foothold in regions experiencing economic growth.
-
Threats:
- Intense Competition from New Entrants: Example: The entry of new competitors with innovative products or disruptive business models poses a threat, requiring the organization to adapt and differentiate itself to maintain market share.
- Economic Downturn Affecting Consumer Spending: Example: During economic downturns, consumers tend to reduce discretionary spending. This threat requires strategic planning to navigate through challenging economic conditions, possibly by diversifying product offerings or adjusting pricing strategies.
Free SWOT Analysis Template:
SWOT Analysis Template: [Your Company Name/Project Name]
Internal Factors (Strengths and Weaknesses):
Strengths:
- Established Brand Reputation:
- [Tip: Consider factors that contribute to your brand’s recognition, customer trust, and market position.]
- Skilled and Motivated Workforce:
- [Tip: Focus on the talents and dedication of your team members that contribute to productivity and innovation.]
- Efficient Operational Processes:
- [Tip: Identify internal processes that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and contribute to overall operational excellence.]
- Advanced Technological Infrastructure:
- [Tip: Highlight the use of up-to-date technology that gives your organization a competitive edge.]
- Strong Financial Stability:
- [Tip: Include financial indicators that showcase stability, such as a consistent revenue stream and prudent financial management.]
Weaknesses:
- Outdated IT Infrastructure:
- [Tip: Acknowledge areas where technology may be outdated and explore potential consequences on operational efficiency.]
- Limited Marketing Budget:
- [Tip: Address constraints in marketing resources and its impact on market visibility and customer outreach.]
- Dependence on a Single Supplier:
- [Tip: Recognize vulnerabilities, such as dependence on a sole supplier, that might pose risks to the supply chain.]
- Lack of Diversification in Product Line:
- [Tip: Consider how a limited product range may affect the organization’s ability to adapt to changing market demands.]
- Inconsistent Quality Control:
- [Tip: Highlight any weaknesses in maintaining consistent quality standards that could affect customer satisfaction.]
External Factors (Opportunities and Threats):
Opportunities:
- Growing Market Demand for Sustainable Products:
- [Tip: Explore emerging trends, such as sustainability, that present opportunities for product development.]
- Global Expansion into Untapped Markets:
- [Tip: Identify regions or markets where there is potential for growth and expansion.]
- Advancements in Technology:
- [Tip: Leverage technological advancements that could enhance products or create new market opportunities.]
- Changes in Regulatory Environment Favoring the Industry:
- [Tip: Be aware of shifts in regulations that could create favorable conditions for your industry.]
- Collaboration Opportunities with Industry Leaders:
- [Tip: Explore partnerships with established industry leaders that could enhance your market presence.]
Threats:
- Intense Competition from New Entrants:
- [Tip: Assess the competitive landscape and potential threats posed by new players entering the market.]
- Economic Downturn Impacting Consumer Spending:
- [Tip: Consider economic factors that may affect consumer behavior and spending patterns.]
- Rapid Technological Changes:
- [Tip: Anticipate how swift technological changes may impact your industry and organizational operations.]
- Supply Chain Disruptions:
- [Tip: Recognize vulnerabilities in the supply chain that could disrupt operations, such as geopolitical events or natural disasters.]
- Negative Public Perception Due to Industry Issues:
- [Tip: Be aware of industry-related challenges that may contribute to negative public perception and reputation risks.]
Instructions:
- [Tip: Encourage a collaborative approach, involving team members from various departments.]
- [Tip: Prioritize factors based on their importance and potential impact.]
- [Tip: Use the analysis to inform strategic decision-making and planning.]
Feel free to customize this template based on the specific needs and nuances of your organization or project.
On a Final Note,
SWOT analysis emerges as a dynamic compass guiding organizations through the intricate paths of the business terrain. By delving into internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats, businesses gain the foresight needed for informed decision-making and strategic prowess. This tool is not just a guide; it is a key to unlocking the latent potential within your organization. Embrace the transformative power of SWOT analysis to chart a course that propels your business forward, enabling it to not only adapt to challenges but to flourish in the ever-evolving competitive landscape.


